Vgrid Expressions
Vgrid DGGS Expressions is integrated into QGIS field calculator¶
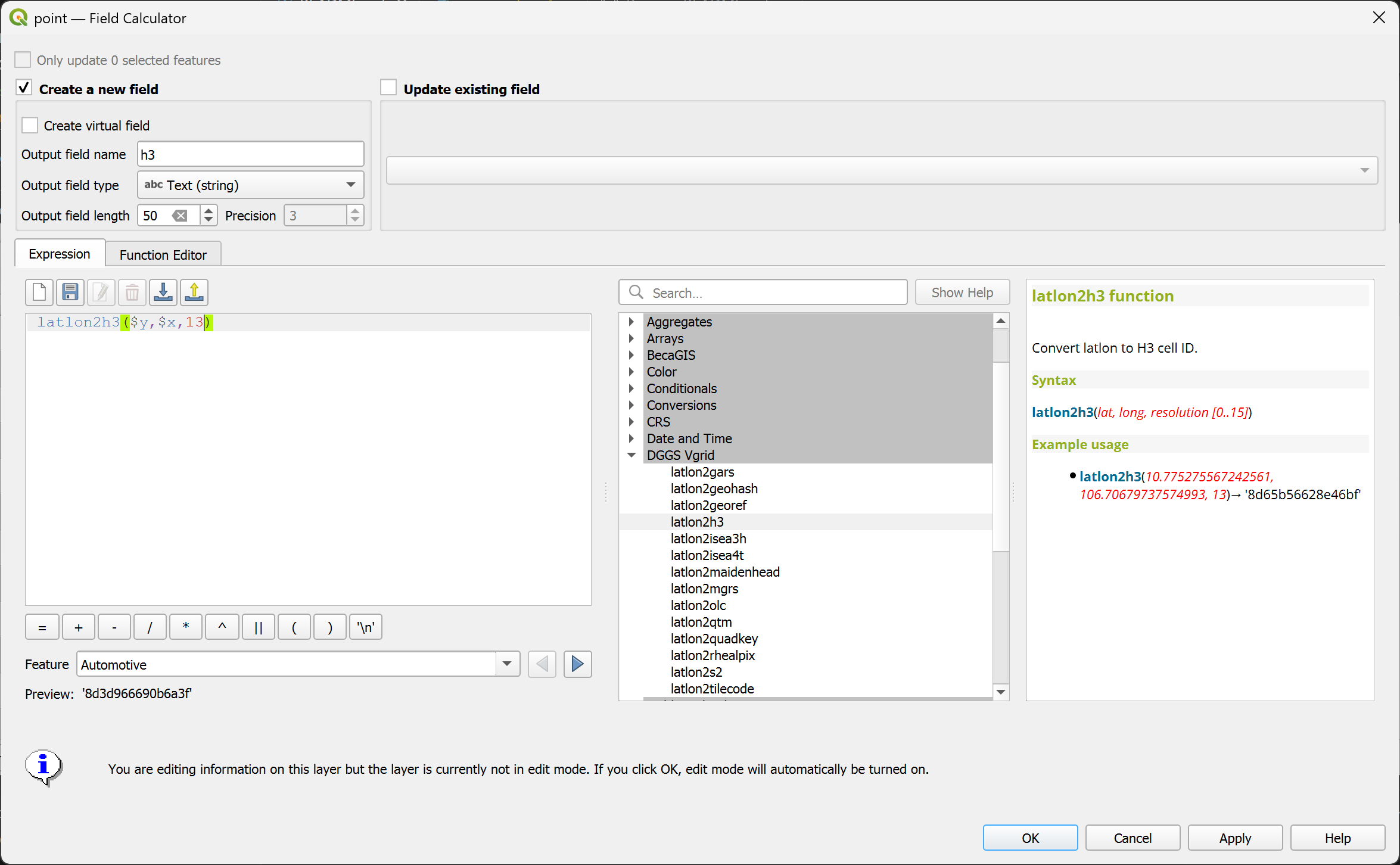
latlon2h3¶
Convert (lat, long) to H3 ID.
Syntax
latlon2h3(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: H3 resolution [0..15]
Example usage
latlon2h3(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 13) → '8d65b56628e46bf'
Point features: latlon2h3($y, $x, 13)
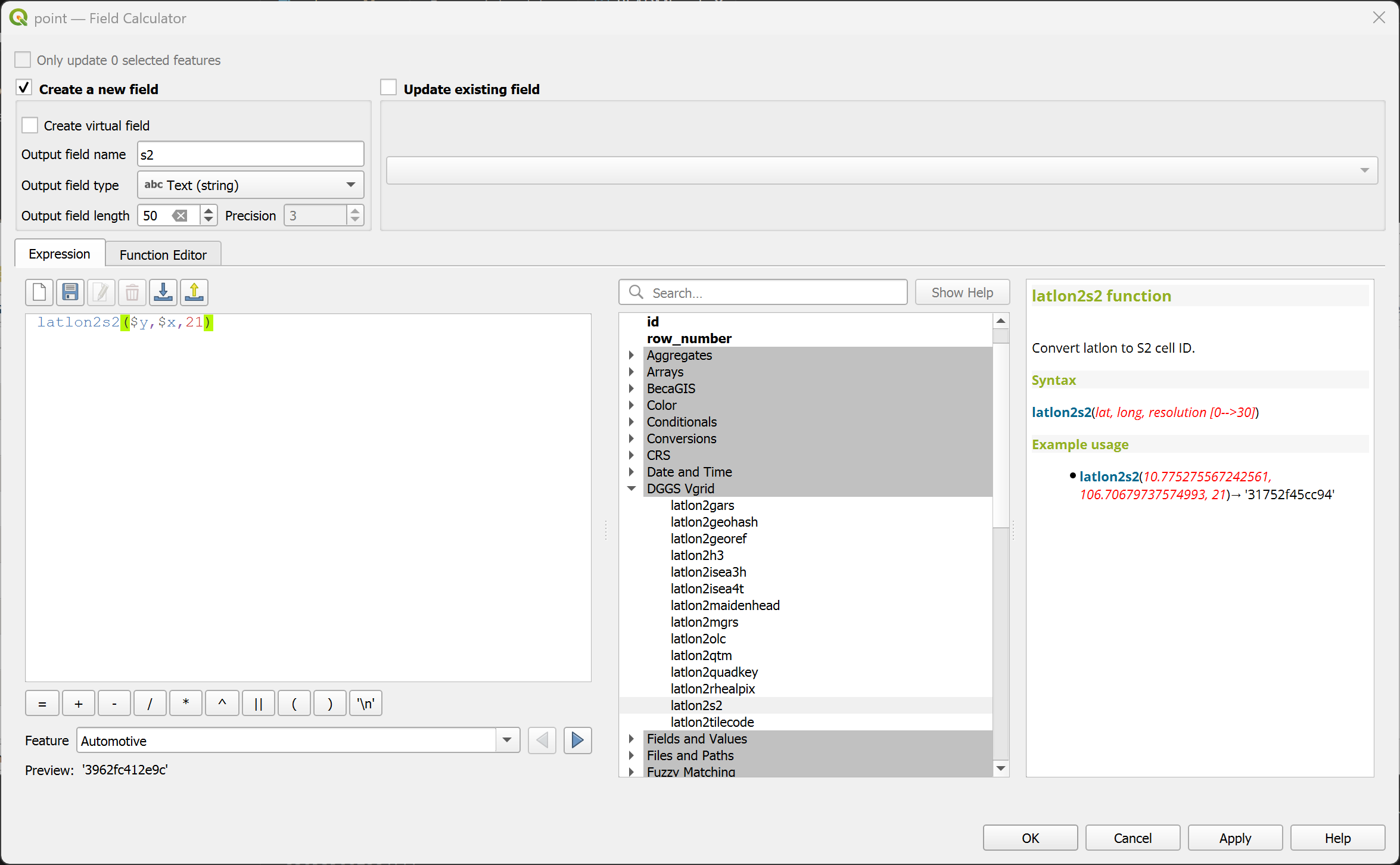
latlon2s2¶
Convert (lat, long) to S2 Token.
Syntax
latlon2s2(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: S2 resolution [0..30]
Example usage
latlon2s2(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 21) → '31752f45cc94'
Point features: latlon2s2($y, $x, 21)
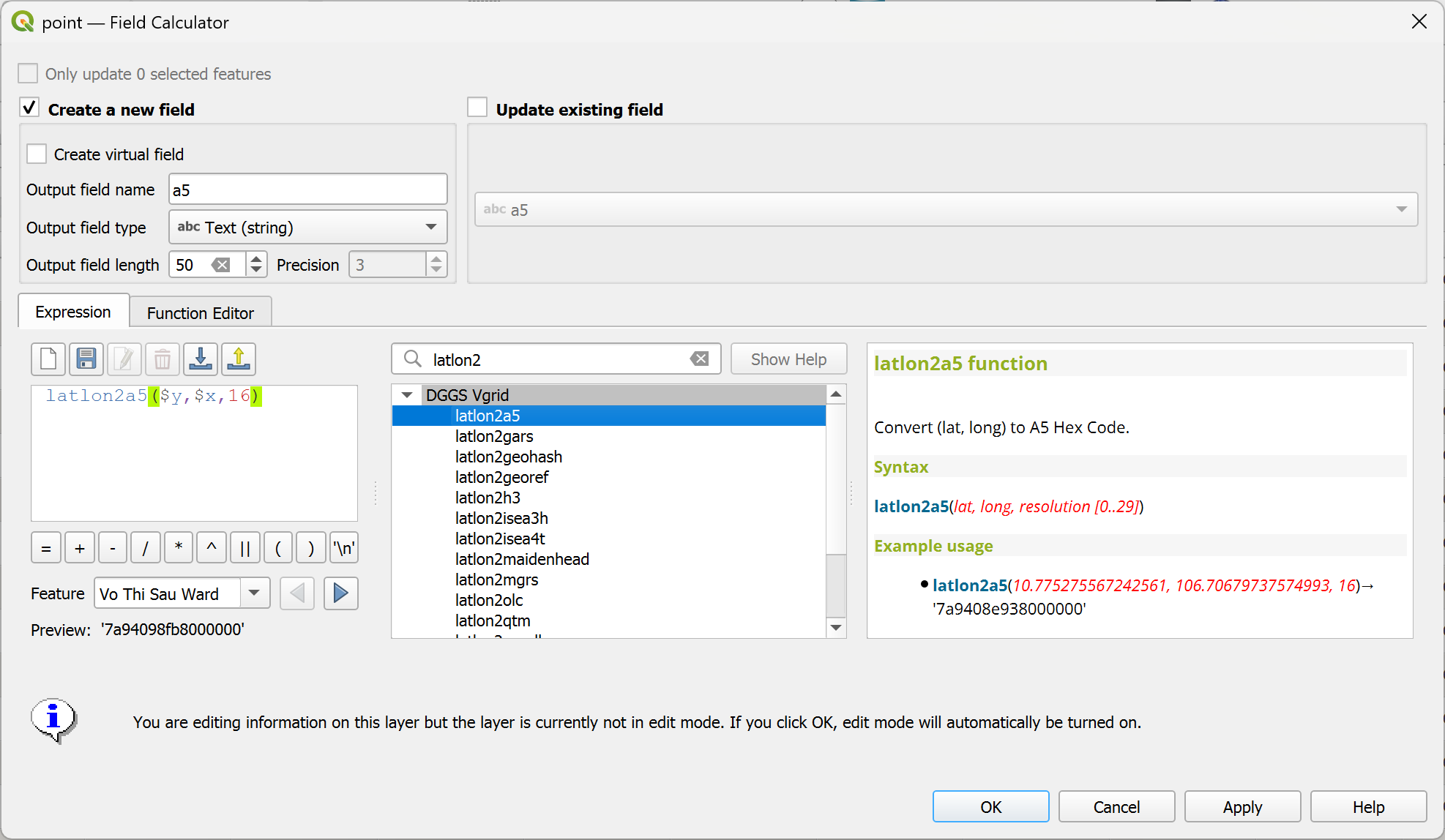
latlon2a5¶
Convert (lat, long) to A5 Hex.
Syntax
latlon2a5(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: A5 resolution [0..29]
Example usage
latlon2a5(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 16) → '7a9408e938000000'
Point features: latlon2a5($y, $x, 16)
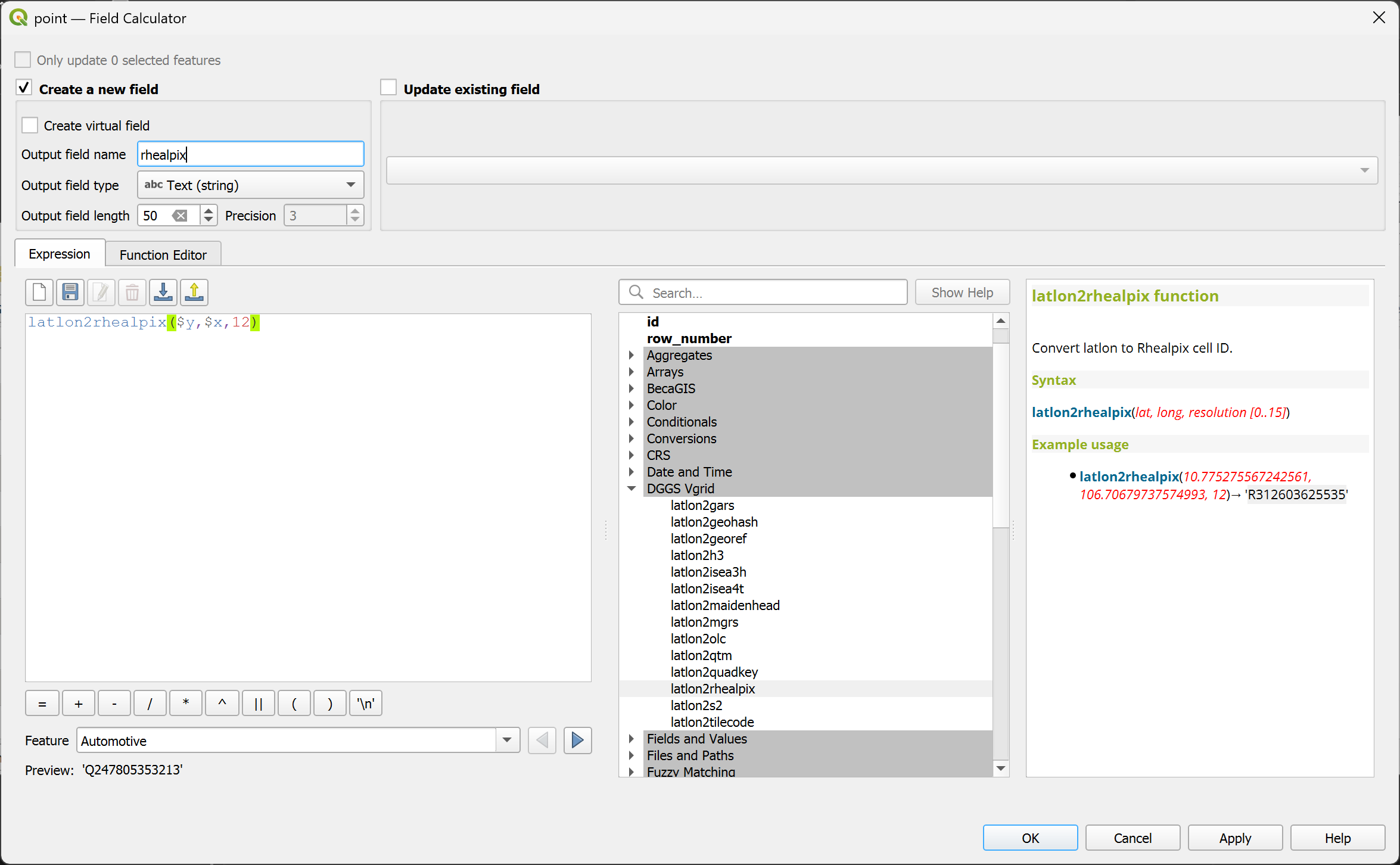
latlon2rhealpix¶
Convert (lat, long) to rHEALPix ID.
Syntax
latlon2rhealpix(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: rHEALPix resolution [0..15]
Example usage
latlon2rhealpix(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 12) → 'R312603625535'
Point features: latlon2rhealpix($y, $x, 12)
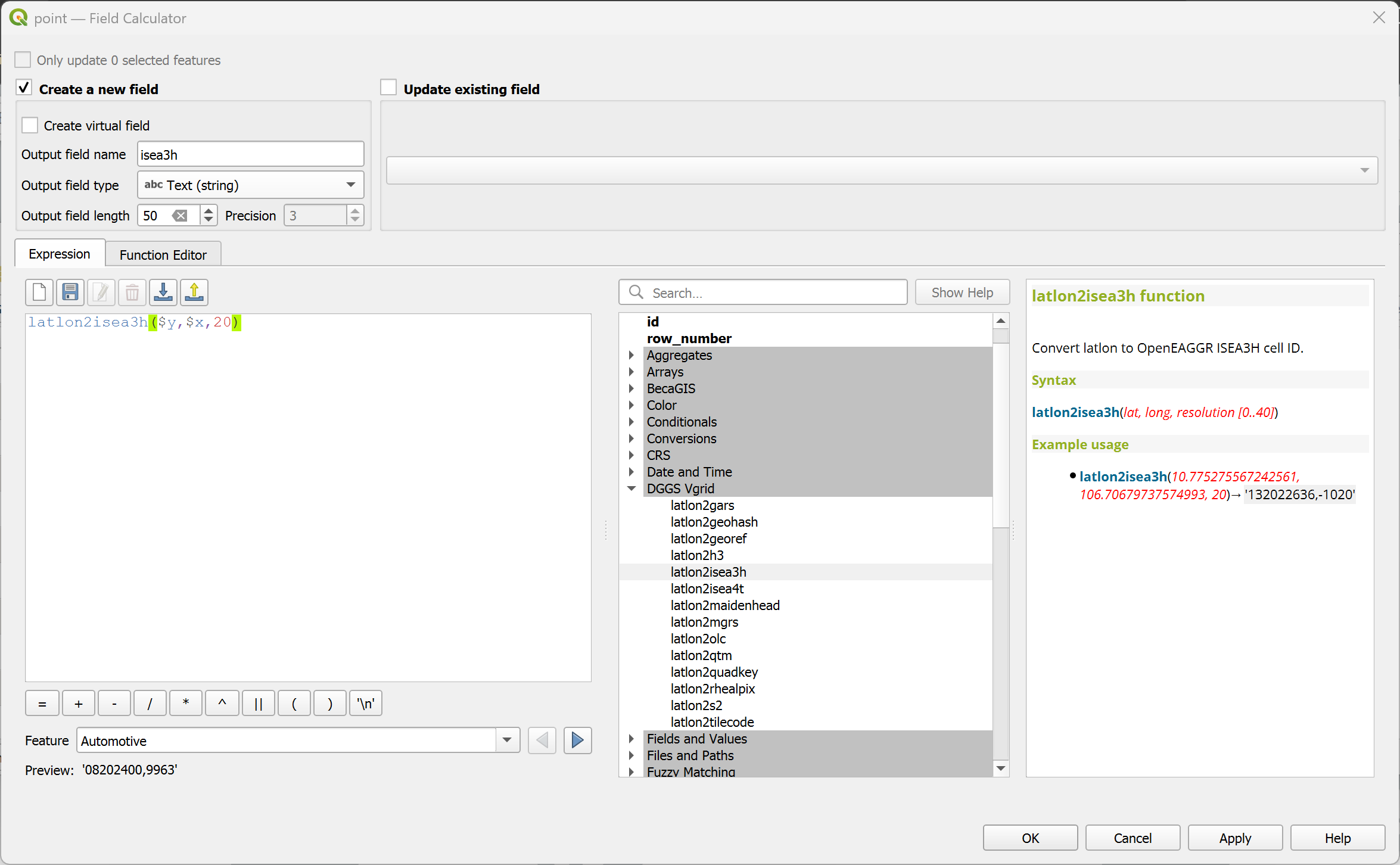
latlon2isea4t¶
Convert (lat, long) to OpenEAGGR ISEA4T ID (Windows only).
Syntax
latlon2isea4t(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: ISEA4T resolution [0..39]
Example usage
latlon2isea4t(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 20) → '1310231333101123322130'
Point features: latlon2isea4t($y, $x, 20)
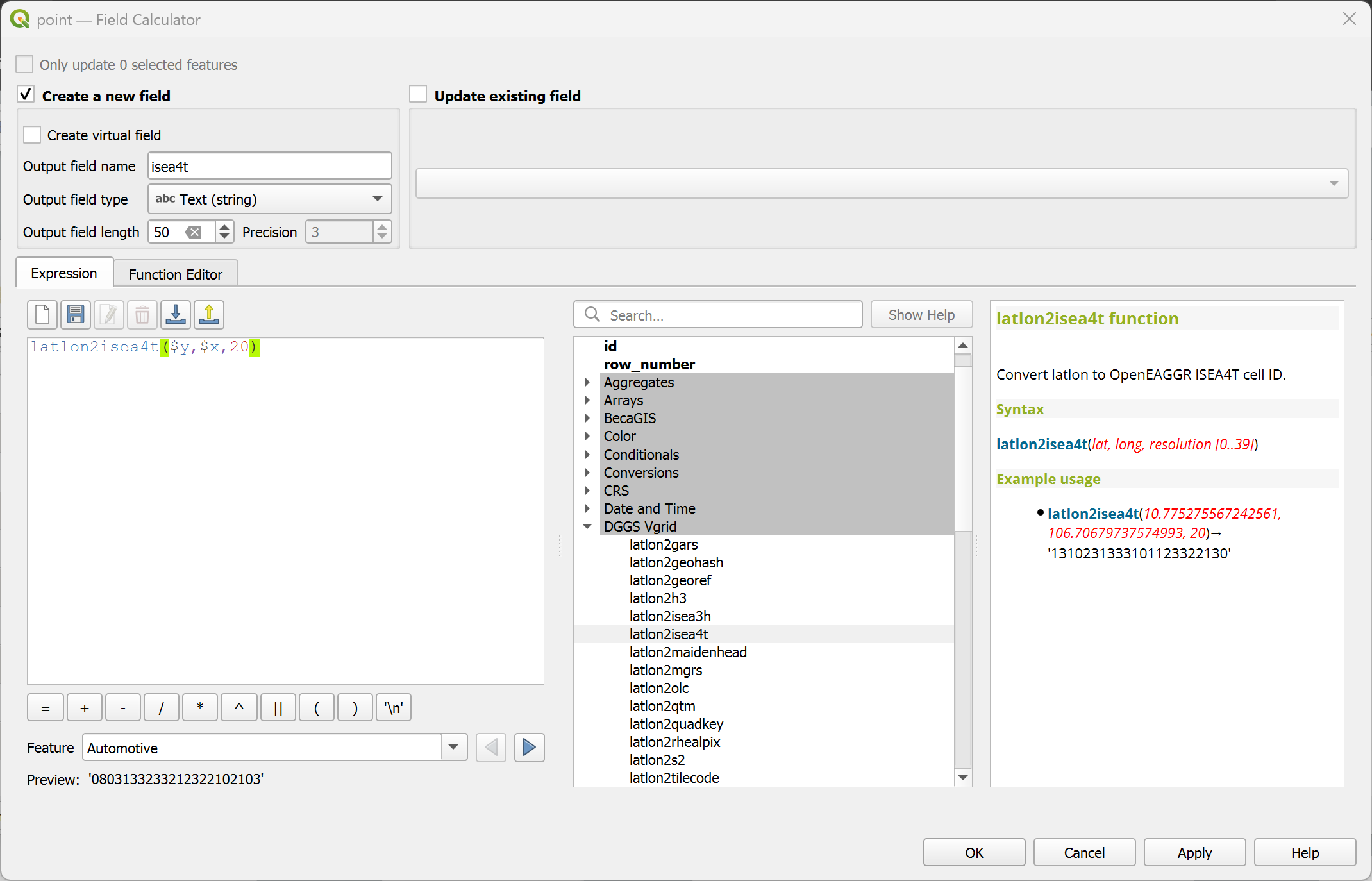
latlon2isea3h¶
Convert (lat, long) to OpenEAGGR ISEA3H ID (Windows only).
Syntax
latlon2isea3h(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: ISEA3H resolution [0..40]
Example usage
latlon2isea3h(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 20) → '132022636,-1020'
Point features: latlon2isea3h($y, $x, 20)
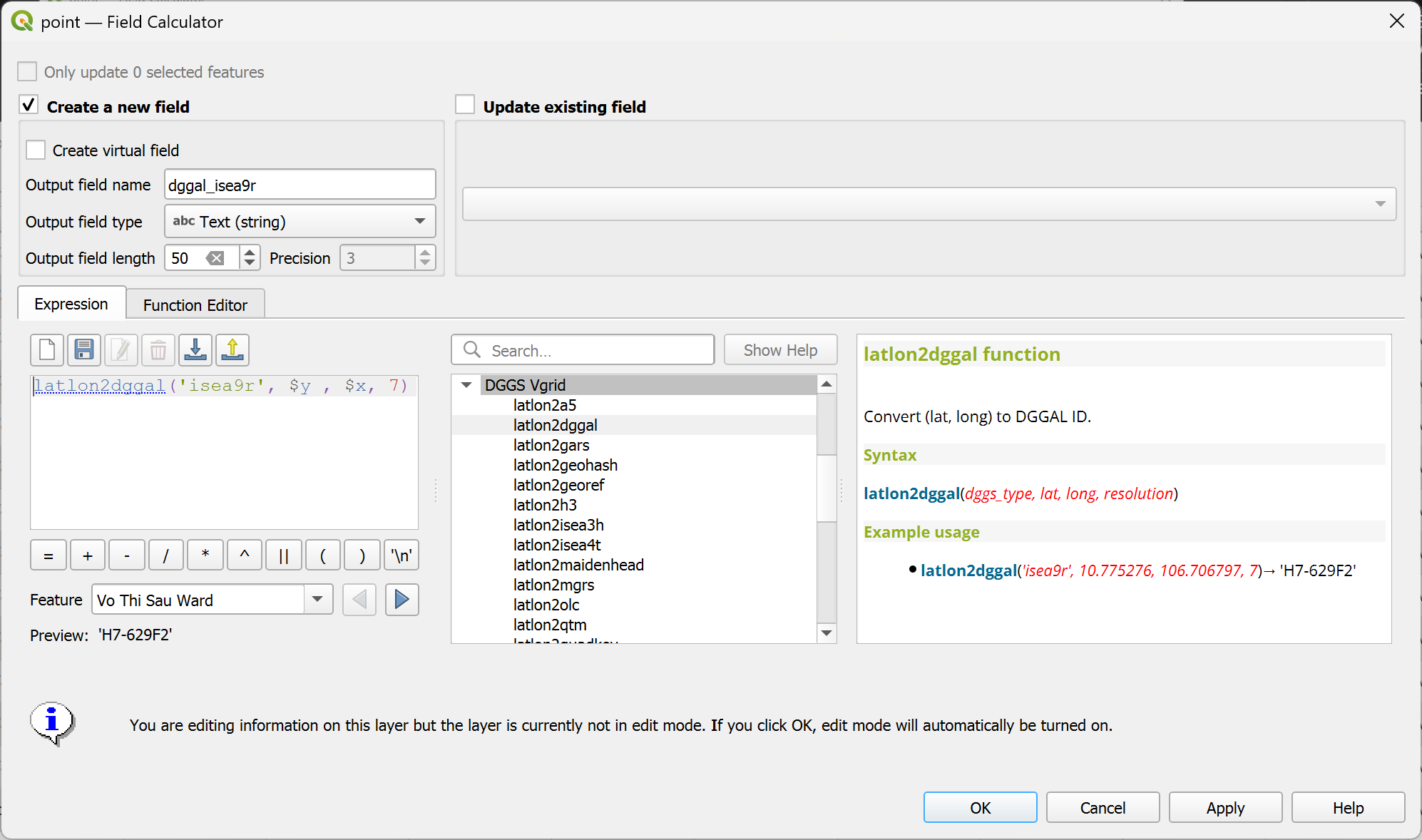
latlon2dggal¶
Convert (lat, long) to DGGAL ID.
Syntax
latlon2dggal(dggs_type, lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
dggs_type: DGGS type ('gnosis','isea3h','isea9r','ivea3h','ivea9r','rtea3h','rtea9r','rhealpix')
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: DGGS resolution
Example usage
latlon2dggal('isea9r', 10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 7) → 'H7-629F2'
Point features: latlon2dggal('isea9r', $y, $x, 7)
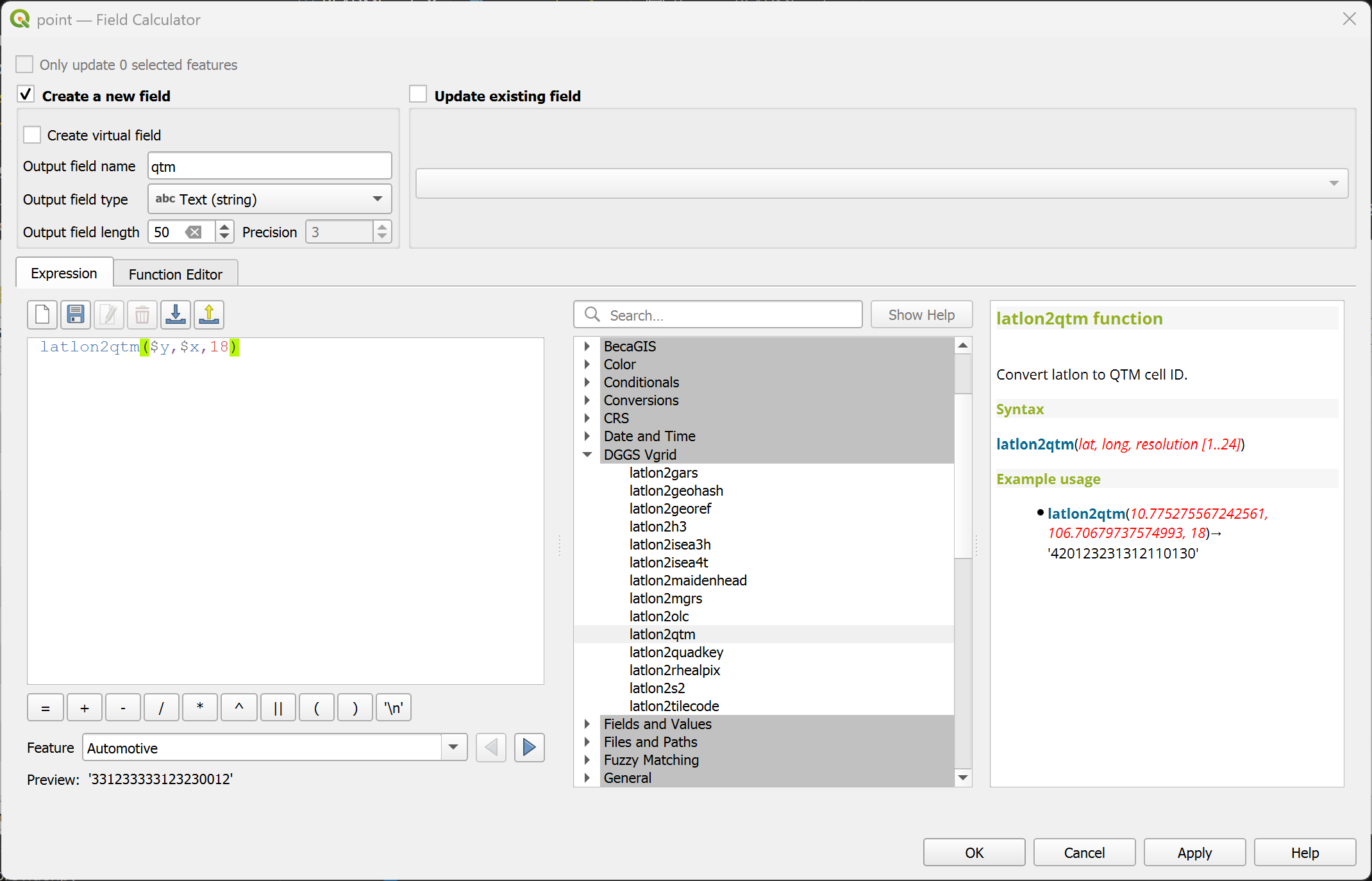
latlon2qtm¶
Convert (lat, long) to QTM.
Syntax
latlon2qtm(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: QTM resolution [1..24]
Example usage
latlon2qtm(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 18) → '420123231312110130'
Point features: latlon2qtm($y, $x, 18)
latlon2olc¶
Convert (lat, long) to Open Location Code (OLC)/ Google Plus Code.
Syntax
latlon2olc(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: OLC resolution [2,4,6,8,10,11..15]
Example usage
latlon2olc(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 11) → '7P28QPG4+4P7'
Point features: latlon2olc($y, $x, 11)
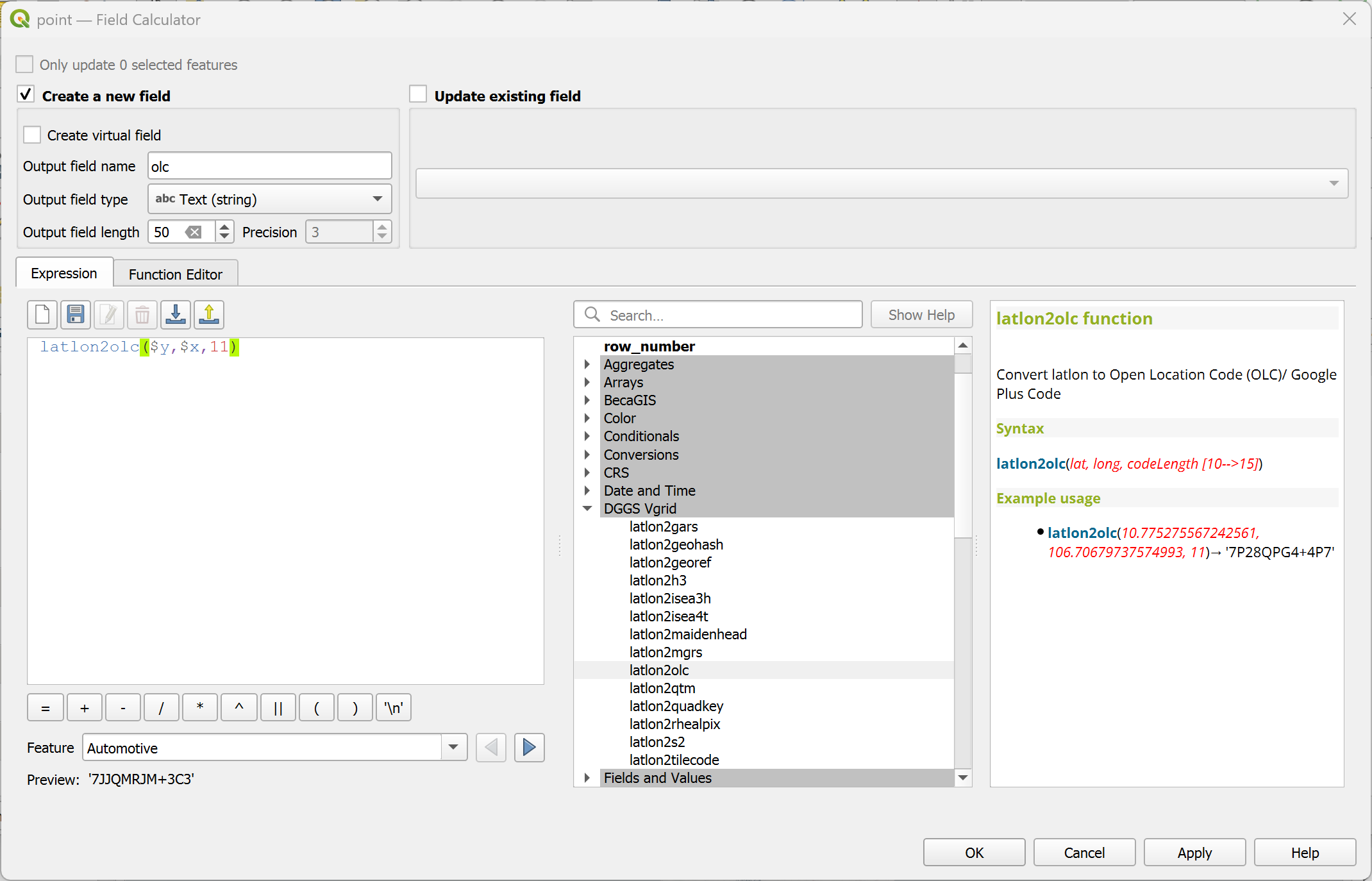
latlon2geohash¶
Convert (lat, long) to Geohash ID.
Syntax
latlon2geohash(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: Geohash resolution [1..30]
Example usage
latlon2geohash(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 9) → 'w3gvk1td8'
Point features: latlon2geohash($y, $x, 9)
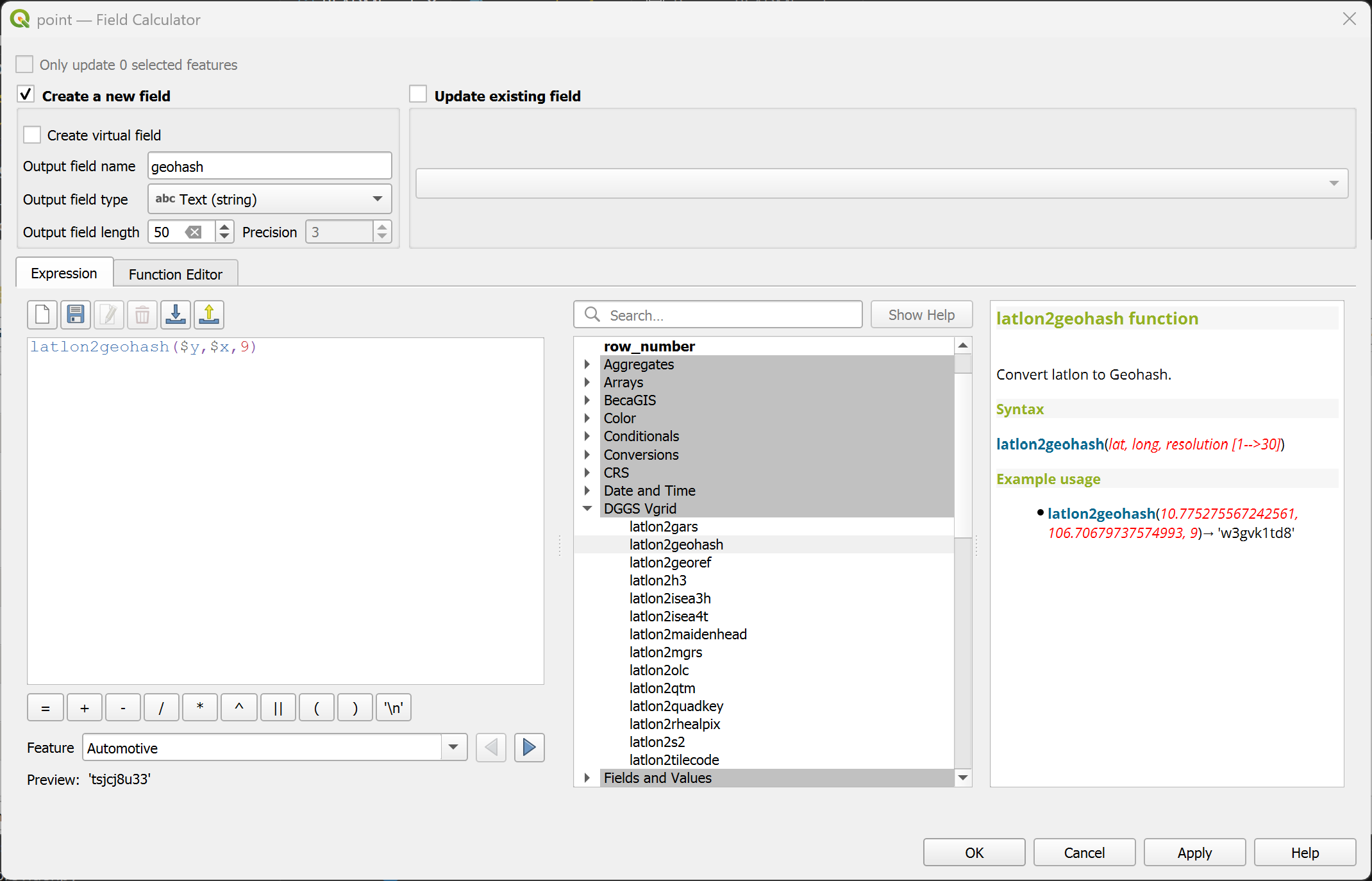
latlon2georef¶
Convert (lat, long) to GEOREF ID.
Syntax
latlon2georef(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: GEOREF resolution [0..10]
Example usage
latlon2georef(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 5) → 'VGBL4240746516'
Point features: latlon2georef($y, $x, 5)
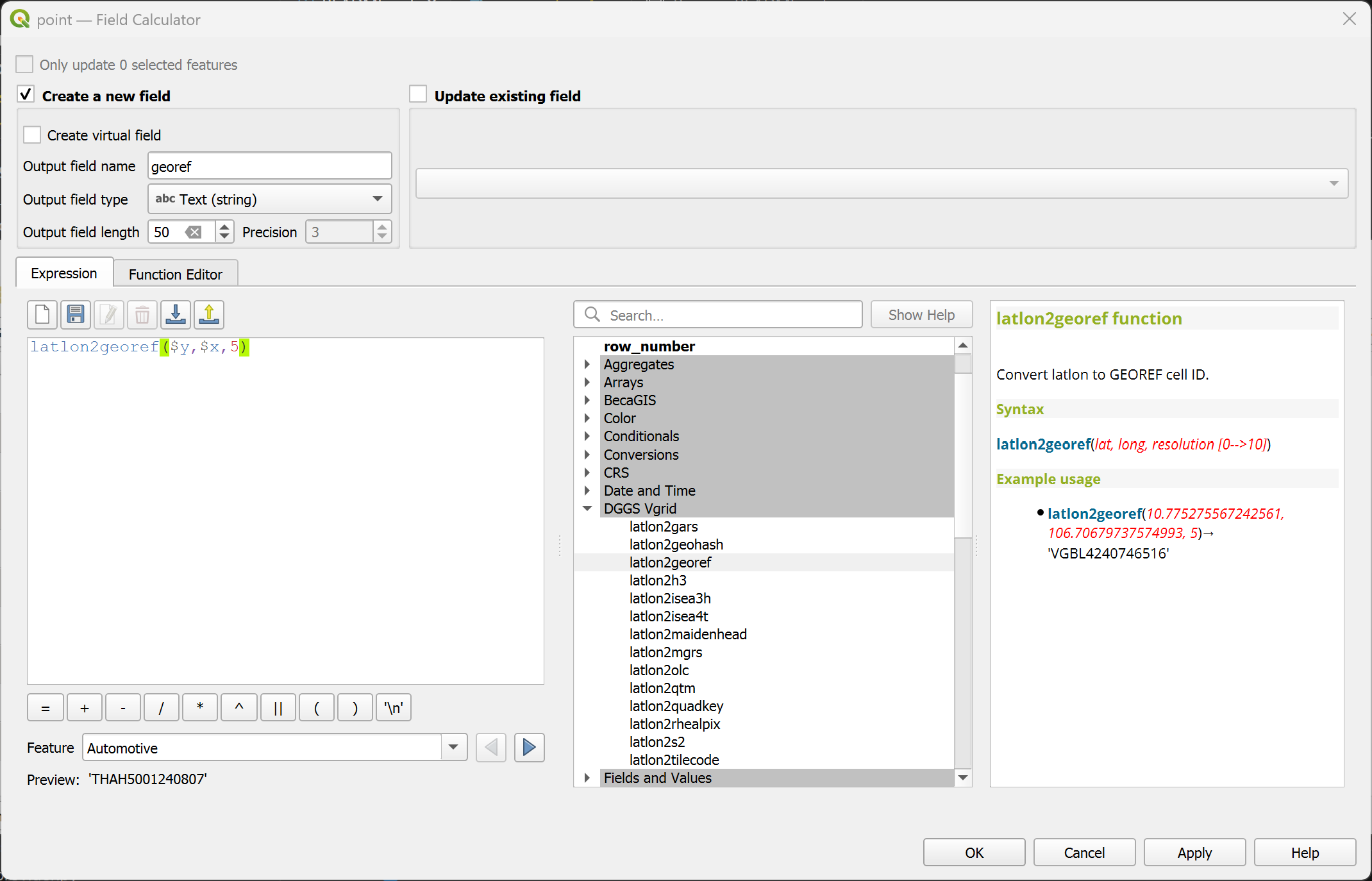
latlon2mgrs¶
Convert (lat, long) to MGRS ID.
Syntax
latlon2mgrs(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: MGRS resolution [0..5]
Example usage
latlon2mgrs(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 4) → '48PXS86629165'
Point features: latlon2mgrs($y, $x, 4)
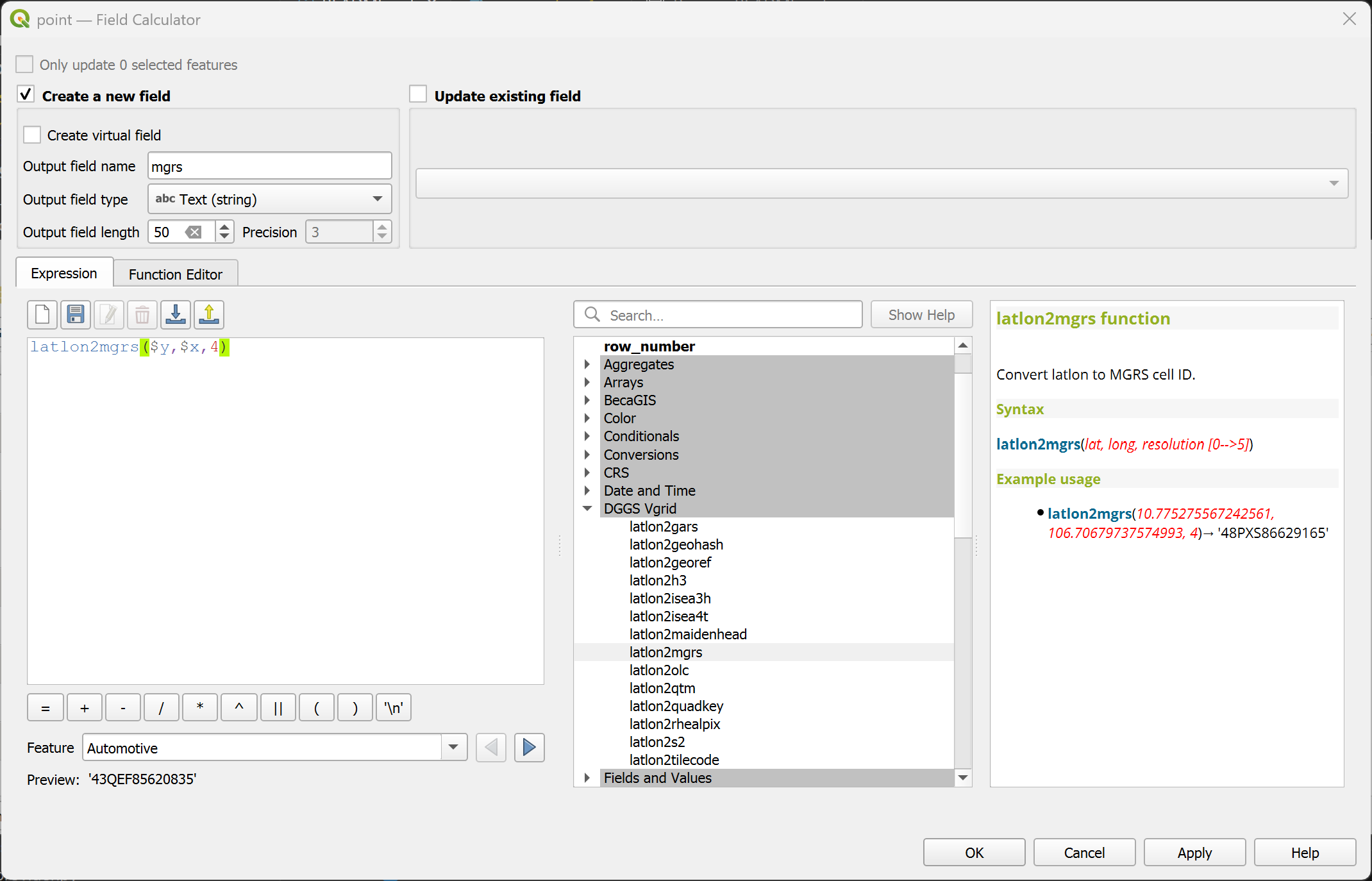
latlon2tilecode¶
Convert (lat, long) to Tilecode ID.
Syntax
latlon2tilecode(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: Tilecode resolution [0..29]
Example usage
latlon2tilecode(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 23) → 'z23x6680752y3941728'
Point features: latlon2tilecode($y, $x, 23)
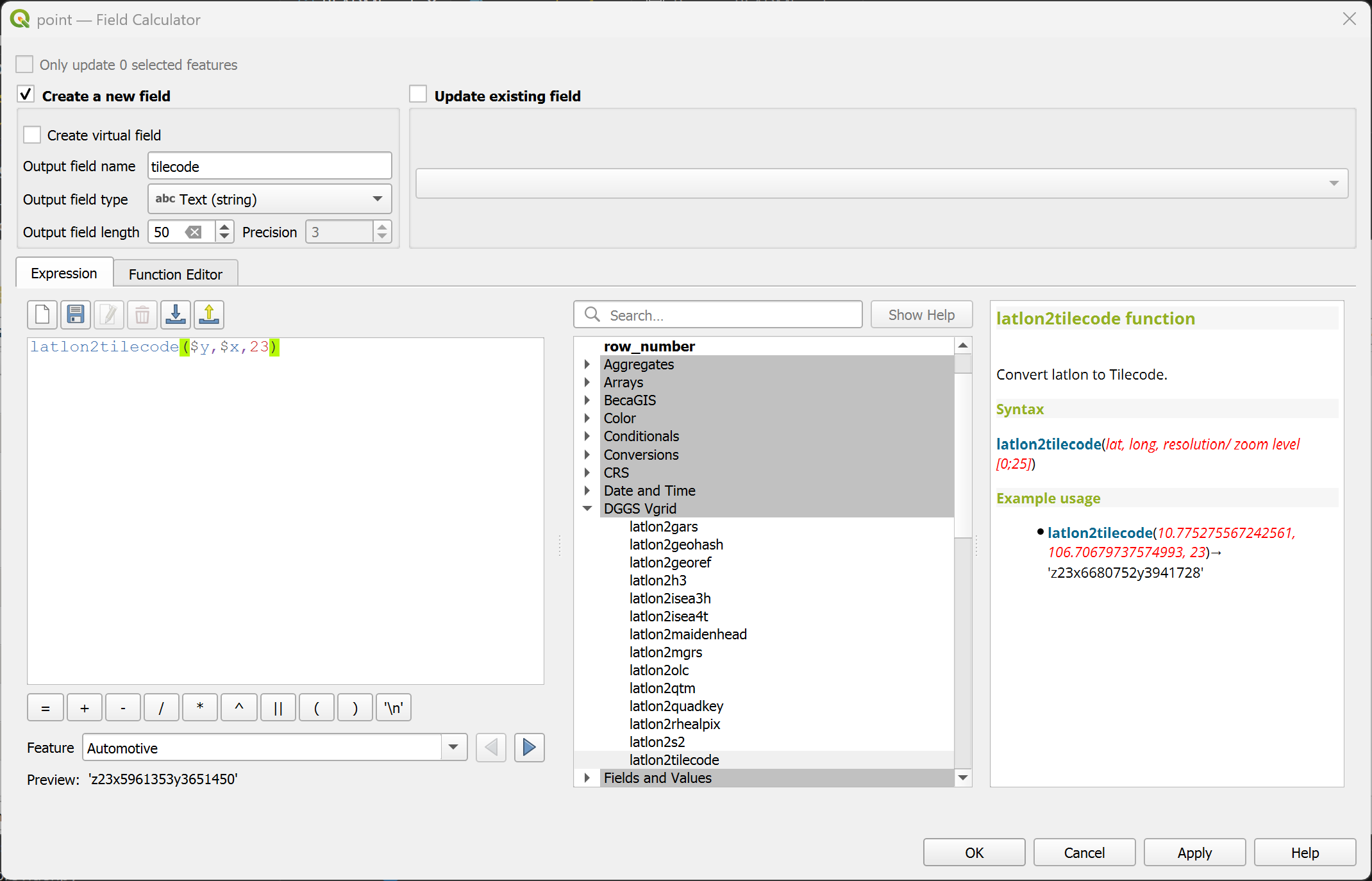
latlon2quadkey¶
Convert (lat, long) to Quadkey ID.
Syntax
latlon2quadkey(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: Quadkey resolution [0..29]
Example usage
latlon2quadkey(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 23) → '13223011131020212310000'
Point features: latlon2quadkey($y, $x, 23)
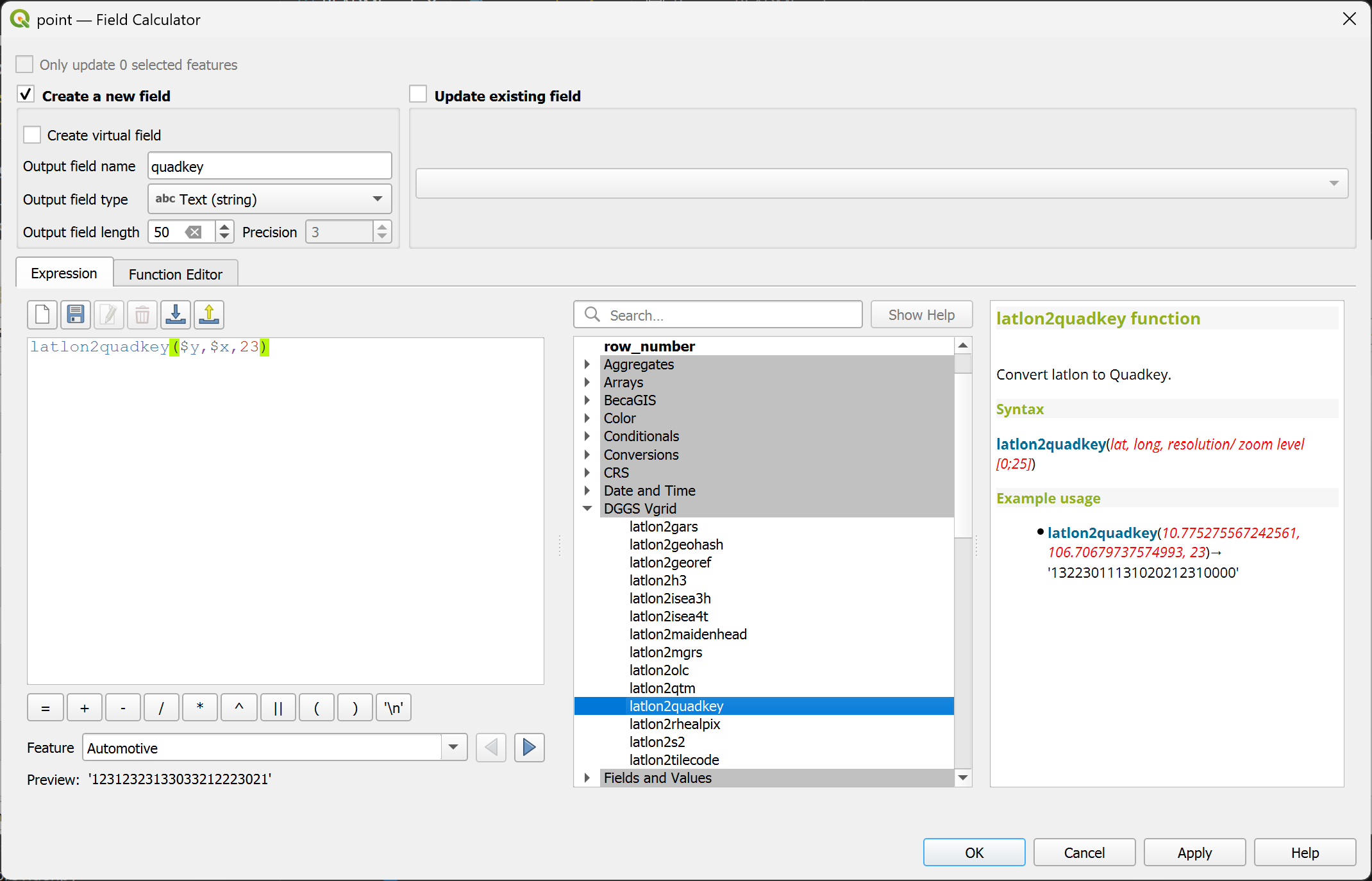
latlon2maidenhead¶
Convert (lat, long) to Maidenhead ID.
Syntax
latlon2maidenhead(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: Maidenhead resolution [1..4]
Example usage
latlon2maidenhead(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 4) → 'OK30is46'
Point features: latlon2maidenhead($y, $x, 4)
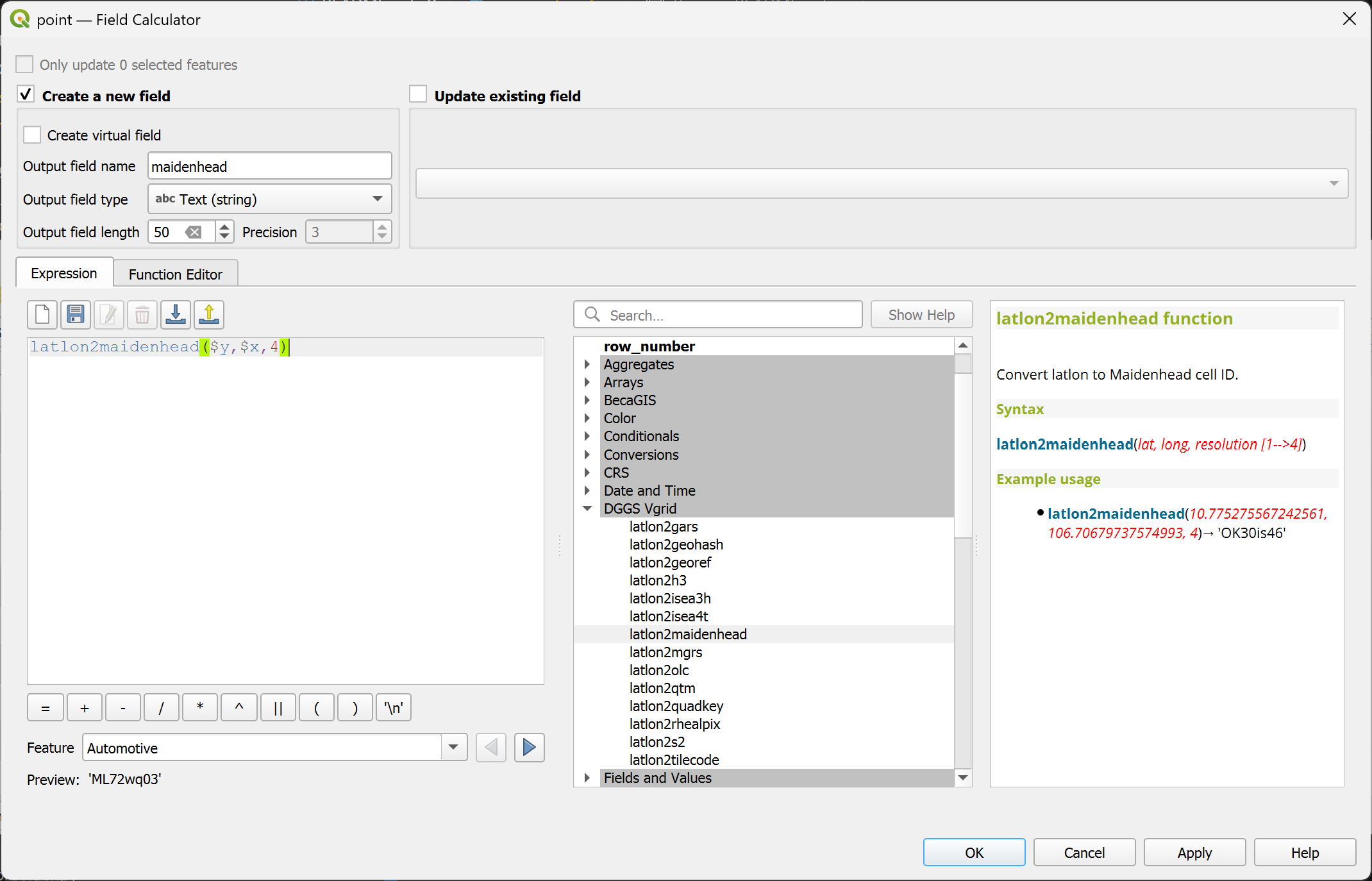
latlon2gars¶
Convert (lat, long) to GARS Code.
Syntax
latlon2gars(lat, long, resolution)
Arguments
lat: latitude coordinate field or value
long: longitude coordinate field or value
resolution: GARS resolution [1..4] (30, 15, 5, 1 minutes)
Example usage
latlon2gars(10.775275567242561, 106.70679737574993, 4) → '574JK1918'
Point features: latlon2gars($y, $x, 4)
comp_pp¶
Calculate Polsby–Popper (PP) Compactness.¶
Polsby-Popper Compactness is the ratio of the area A of the geometry to the area of a circle whose circumference is equal to the perimeter P of the geometry.
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_pp(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_pp($geometry) → [0..1]
comp_schwartz¶
Calculate Schwartzberg Compactness.¶
Schwartzberg Compactness is the ratio of the perimeter P of the geometry to the circumference of a circle whose area is equal to the area of the geometry
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_schwartz(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_schwartz($geometry) → [0..1]
comp_reock¶
Calculate Reock Compactness.¶
Reock is the ratio of the area A of the geometry to the area of its minimum bounding circle \(A_{\text{mbc}}\).
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_reock(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_reock($geometry) → [0..1]
comp_box_reock¶
Calculate Box Reock Compactness.¶
Box Reock is the ratio of the area A of the geometry to the area of its minimum bounding rectangle \(A_{\text{mbr}}\).
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_box_reock(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_box_reock($geometry) → [0..1]
comp_cvh¶
Calculate Convex Hull Compactness. Convex Hull Compactness is the ratio of the area A of the geometry to the area of its convex hull \(A_{\text{cvh}}\)
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_cvh(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_cvh($geometry) → [0..1]
comp_skew¶
Calculate Skew Compactness.¶
Skew Compactness is the ratio of the area \(A_{\text{mic}}\) of the maximum inscribed circle to the area of the minimum bounding circle \(A_{\text{mbc}}\).
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_skew(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_skew($geometry) → [0..1]
comp_x_sym¶
Calculate X‑Symmetry Compactness.¶
X-Symmetry compactness is calculated by dividing the intersection area \(A\bigl(I(G,G^X)\bigr)\) of the geometry with its reflection across the horizontal axis (x-axis) by the area of the original geometry A.
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_x_sym(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_x_sym($geometry) → [0..1]
comp_y_sym¶
Calculate Y‑Symmetry Compactness.¶
Y-Symmetry compactness is calculated by dividing the intersection area \(A\bigl(I(G,G^Y)\bigr)\) of the geometry with its reflection across the vertical axis (y-axis) by the area of the original geometry A.
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_y_sym(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_y_sym($geometry) → [0..1]
comp_lw¶
Calculate Length–Width Compactness.¶
Length–Width Compactness is the ratio of the width \(W_{\text{mbr}}\) to the length \(L_{\text{mbr}}\) of the geometry’s minimum bounding rectangle.
Scores range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the least compact and 1 is the most compact.
Syntax
comp_lw(geometry)
Arguments
geometry: a polygon geometry
Example usage
comp_lw($geometry) → [0..1]